Introduction
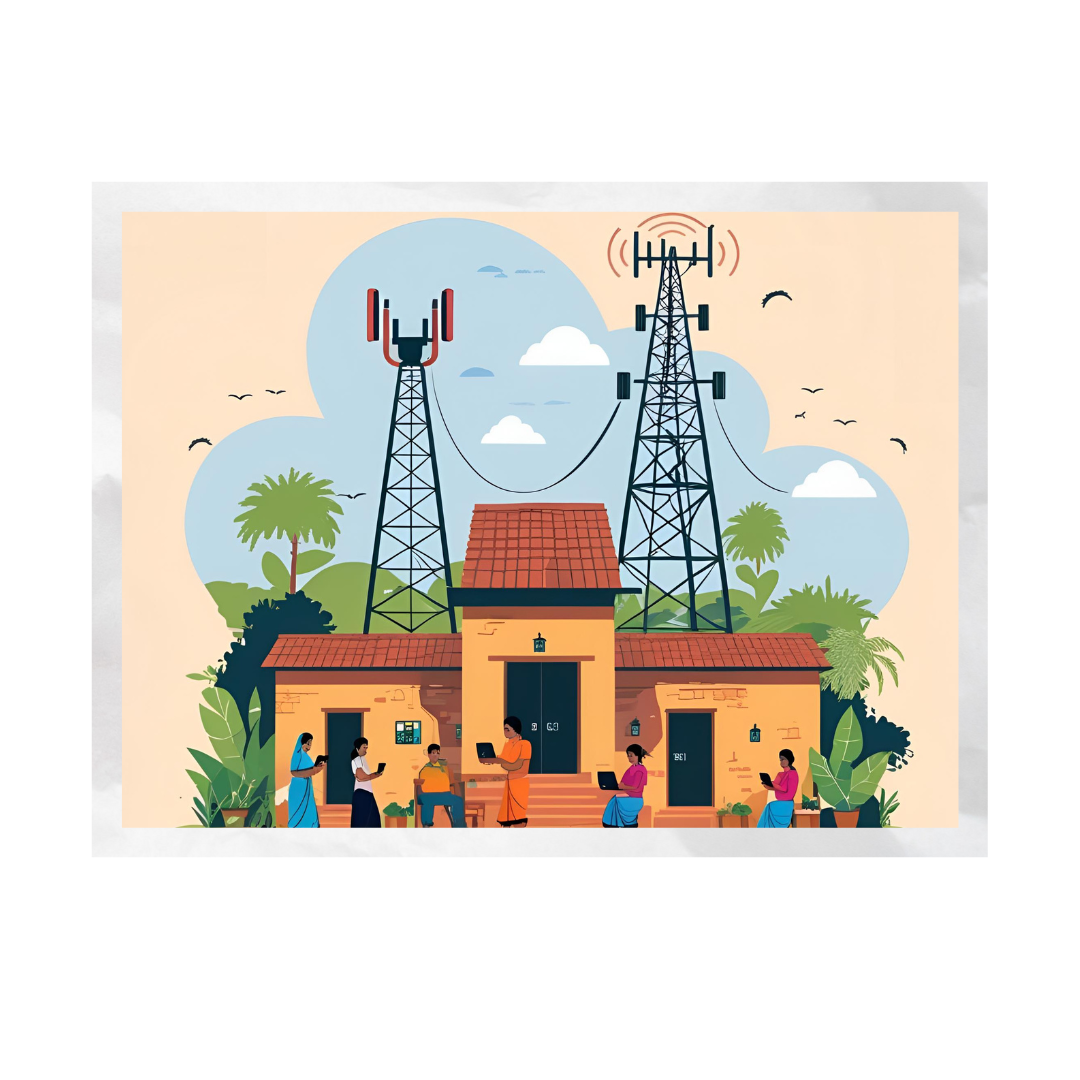
India’s digital revolution has made significant strides, yet a substantial portion of its rural population remains disconnected. As of 2024, rural areas account for 55% of India’s 886 million active internet users, surpassing urban regions . Despite this growth, challenges persist in achieving universal internet access across the country’s diverse landscapes.
Current Landscape of Rural Internet Connectivity
- User Base Growth: The number of internet users in India has risen from 574 million in 2019 to 886 million in 2024, with rural areas contributing significantly to this increase.
- Daily Usage: On average, Indians spend 91 minutes online daily, with rural users closely matching urban counterparts in usage patterns.
- Gender Gap: The digital gender divide is narrowing, with females comprising 47% of the internet user base.
Challenges in Rural Internet Deployment
- Infrastructure Limitations:
- High costs and logistical challenges hinder the deployment of broadband infrastructure in remote areas.
- Geographical Barriers:
- Diverse terrains, including mountains and forests, complicate network expansion efforts.
- Digital Literacy:
- Limited awareness and understanding of digital technologies impede adoption in rural communities.
- Economic Constraints:
- Affordability of devices and internet services remains a significant barrier for many rural residents.
Government Initiatives to Enhance Connectivity
- BharatNet Project: Aims to provide broadband connectivity to all Gram Panchayats, enhancing digital access in rural areas.
- National Broadband Mission (NBM): Launched to accelerate broadband infrastructure development across the country.
- Digital Bharat Nidhi: Funds projects to improve mobile and internet connectivity in underserved regions.
Role of Private Sector and Innovations
- Satellite Internet Services: Companies like Starlink and Amazon’s Kuiper are exploring satellite-based internet solutions to reach remote areas, offering faster deployment and broader coverage.
- Public Wi-Fi Initiatives: Programs like PM-WANI aim to establish public Wi-Fi hotspots, enhancing internet accessibility in rural regions.
Impact on Rural Communities
- Education: Improved internet access facilitates online learning opportunities, bridging educational gaps.
- Healthcare: Telemedicine services become more accessible, improving healthcare delivery in remote areas.
- Economic Opportunities: Digital connectivity enables e-commerce and remote work, contributing to rural economic development.
Conclusion
While significant progress has been made in expanding internet connectivity in rural India, ongoing efforts are essential to overcome persistent challenges. Collaborative initiatives between the government, private sector, and communities are vital to ensure inclusive digital growth and bridge the digital divide.
📚 References
- Internet and Mobile Association of India (IAMAI) & Kantar. (2024). Internet in India 2024 Report. Link
- Press Information Bureau. (2024). Government’s Efforts to Improve Broadband Connectivity in Rural Areas. Link
- Economic Times. (2025). India’s internet user base to surpass 900 million by 2025 driven by rural growth. Link
- Excitel. (2023). Broadband internet in rural areas: Challenges and solutions. Link
- MIT Sloan. (2024). Expanding Internet Adoption in Rural India. Link




Leave a Reply